Whitepaper
Redefining Ownership, Access, and Trust in the Digital Era
NFToa
The NFT open access, —a new paradigm for how NFTs are used
Abstract
In the current NFT landscape, most tokens are limited to being digital collectibles. People buy, hold, and resell NFTs primarily for ownership and trading purposes. NFToa introduces a different way to look at NFTs — not only as collectible items, but as functional access keys that unlock applications, features, and digital services on blockchain-based systems.
1. How NFTs Are Commonly Understood Today
For most users, NFTs are known as digital art, profile pictures, or collectibles. Their main value comes from rarity, visual appeal, and resale potential. While some NFTs claim to have “utility,” that utility is often unclear, centralized, or short-lived. As a result, NFTs are widely perceived as assets to collect and trade, not tools to use.
2. The Missing Perspective
Blockchain already provides something powerful: verifiable ownership. However, most applications do not fully use this ownership beyond displaying a token in a wallet. NFToa starts from a simple question: What if owning an NFT meant you automatically gained access to something real?
3. Introducing the NFToa Paradigm
NFToa treats NFTs as digital key passes. Instead of being just collectibles, NFTs can function as access credentials. If you own a specific NFT, an application can verify that ownership on the blockchain and grant access without accounts, passwords, or subscriptions.
4. NFT as a Key Pass
In the NFToa model:
- An NFT represents permission, not just ownership
- Applications check blockchain ownership to grant access
- Access logic is transparent and verifiable
- The NFT becomes a usable object, not just a display asset
This shifts NFTs from “something you hold” to “something you use.”
5. How This Changes the Role of NFTs
NFTs are no longer limited to art or collectibles. They can act as:
- App access passes
- Feature unlock keys
- Membership cards
- Software licenses
- Submission or participation rights
The same NFT can unlock value repeatedly, not just sit in a wallet.
6. How NFToa Works (High Level)
NFToa uses blockchain-based NFT ownership as the source of truth. Applications verify whether a wallet owns a specific NFT. If ownership is valid, access is granted. No personal data is required, and no centralized account system is needed.
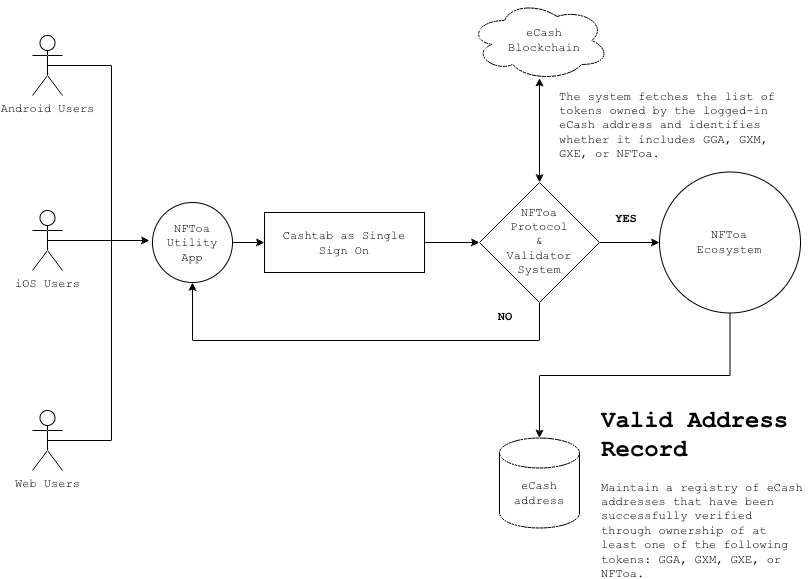
7. Buying and Using Access NFTs
Users acquire NFTs through a simple payment flow. Once the NFT is in the user’s wallet, access is immediate. There is no additional activation, registration, or manual approval. The NFT itself is the key.
8. Why This Matters for Users
- NFTs gain real, practical usefulness
- Ownership has purpose beyond resale
- No need to manage multiple accounts
- Access can persist across devices
- Users control their access through their wallet
9. Why This Matters for Builders
- NFTs become part of the product, not just marketing
- Reduced reliance on user databases
- Clear access rules enforced by blockchain ownership
- New monetization models beyond speculative drops
- Long-term utility aligned with real usage
10. Preventing Empty Utility and Spam
NFToa focuses on meaningful NFT utility. Applications and access NFTs may be reviewed before being promoted or indexed. This helps ensure NFTs represent real access and real functionality, not empty promises or misleading claims.
11. NFToa vs Traditional NFT Usage
Traditional NFTs emphasize collecting and trading. NFToa emphasizes using and accessing. Traditional NFTs often stop at ownership. NFToa starts where ownership becomes functional.
12. The Role of Blockchain
Blockchain provides transparent ownership and verification. NFToa builds on this foundation to make NFTs useful inside applications. Users do not need to understand the technical details — they only need to know that ownership equals access.
13. The Direction of NFToa
NFToa aims to normalize NFTs as access tools, not speculative assets. The goal is to help users and developers see NFTs as part of everyday software, where blockchain ownership unlocks real digital experiences.
14. Conclusion
NFTs do not have to be limited to collectibles. With NFToa, NFTs become keys — usable, verifiable, and functional. This is a shift from owning images to owning access, and from collecting tokens to using them.